Whole Leaf Aloe Vera And The HeartWhile the polysaccharides are the largest single group of Aloe constituents possessing some remarkable actions and activities, they are not alone, but share pharmacological properties with a large number of Aloe constituents. As you may be aware, plants have been the mainstay source of medically important materials (medicines) for literally thousands of years. Among these plants, the Foxglove has a special place because it was the original source of the cardiac glycoside, digitalis. Digitalis works by slowing a runaway heart rhythm as well as increasing the force of the contraction of the heart muscle, especially in cases of congestive cardiomyopathy - (cardio = heart; myo = muscle; pathy = disease) commonly referred to as congestive heart failure. In failing hearts, digitalis offers three potential therapeutic actions: Chronotropic (Heart Rate Effects)Trough Chronotropic (Heart Rate) effects, the heart rate is slowed so the diastolic period (the time between actual muscular contractions [the systolic period]) is longer. It is during the diastolic period that the heart chambers are filled with blood, ready for the next beat. But just as important, this is the time when the heart relaxes and receives its own nourishment. If the heart rate is too fast, the diastolic cardiac nourishment period is too short. This makes the heart less efficient in pumping and circulating blood.Dromotropic (Speed Of Conduction Of The Electrical Impulses Through The Heart)Through the Dromotropic effect, the electrical impulses are slowed. The heart’s electrical impulses permit the atria (top chambers) to beat first, which fills the ventricles with blood, followed by contraction of the ventricles which distributes blood to the body, (The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs while the left ventricle pumps blood to the rest of the body.) Digitalis somewhat slows the conduction velocity through the heart’s electrical system, thus increasing its efficiency and allowing it to work better with less effort.Inotropic (Force Of Heart Contraction)Through the Inotropic effect, the force of the heart contraction is increased. With increased strength in the heart’s contraction, the cardiac output (amount of blood ejected from the right and left ventricles during a single beat) is increased, thus giving the body a better supply of fresh blood... improving circulation and stamina.You may be wondering at this point: Why are we talking about digitalis? Is there digitalis in Aloe juice or extract? The answer, of course, is No. However, the Aloe extract does contain a mineral called calcium isocitrate which is capable of mimicking the positive inotropic action of digitalis, as demonstrated in the isolated cardiac tissues of animals. Indeed, some Japanese researchers isolated this mineral from Aloe saponaria. Recently, it has been shown that this mineral is also found in Aloe aborescens and Aloe barbadensis, but the amount varies among the species. Initially, investigators made some rather crude preparations, which, when tested in isolated rabbit atria (top heart chambers, as explained above), showed a remarkable increase in the force of the contraction (positive inotropic action). (The reason researchers use isolated portions of heart tissue in such studies is to avoid any effects of the nervous system and/or circulating, hormones which, might act with the material being tested and make the results invalid.) With further study and refinement of the material, the researchers were able to identify
the active material in their success in producing the inotropic action with Aloe components. The active material
was shown to be the mineral salt, calcium isocitrate, which had increased the force of contractions in isolated
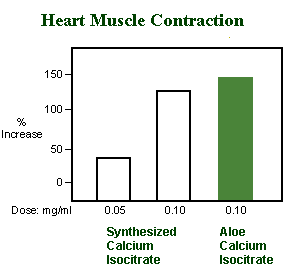
atria tissue from guinea pigs. To confirm their findings, the researchers synthesized the calcium isocitrate and tested its activity using the same types of isolated heart tissue. The results, as the graph shows, duplicated those produced with the material extracted from Aloe juice. Interestingly, other salts from the Aloe juice also showed positive inotropic activity. Studies have also shown that calcium citrate, a salt advocated for the treatment of osteoporosis (a condition found in older women which causes bones to lose calcium and become weak and brittle), is well absorbed by the human gastrointestinal tract. Some researchers believe that the human body absorbs the calcium isocitrates just as well as it does the calcium citrate. However, no data from studies in human subjects, are available to confirm this belief. The presence of this beneficial compound is no surprise to Aloe researchers. All of these salts are insoluble in alcohol and thus, would be expected to be found in the polysaccharide Aloe fractions precipitated with alcohol in the laboratory. Reference Whole Leaf Aloe Vera And The Heart |
Whole Leaf Aloe Vera - Home Whole Leaf Aloe Vera Products Aloe Vera Information